Embark on an enlightening exploration of course 3 chapter 5 triangles and the pythagorean theorem, where the captivating world of geometry and mathematics intertwines to reveal profound insights and practical applications.
This comprehensive chapter delves into the fundamental concepts of triangles, unraveling their properties, classifications, and real-world significance. The legendary Pythagorean Theorem takes center stage, illuminating its pivotal role in solving right triangle problems and its far-reaching applications across diverse fields.
Triangles

Triangles are three-sided polygons that are defined by three vertices and three sides. They are one of the most basic and important geometric shapes, with numerous applications in various fields.
Triangles have several fundamental properties:
- The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles.
- The side opposite the largest angle is the longest side, and the side opposite the smallest angle is the shortest side.
Triangles are classified into different types based on their side lengths and angle measures:
- Equilateral triangle:All three sides are equal in length, and all three angles are 60 degrees.
- Isosceles triangle:Two sides are equal in length, and the angles opposite the equal sides are equal.
- Scalene triangle:All three sides are different in length, and all three angles are different.
- Right triangle:One angle is 90 degrees.
- Obtuse triangle:One angle is greater than 90 degrees.
- Acute triangle:All three angles are less than 90 degrees.
Triangles are widely used in real-world applications, such as:
- Architecture:Triangles provide structural support and stability to buildings and bridges.
- Engineering:Triangles are used in the design of bridges, airplanes, and other structures.
- Surveying:Triangles are used to measure distances and angles in land surveying.
- Navigation:Triangles are used in navigation systems to determine the position and direction of ships and aircraft.
Pythagorean Theorem
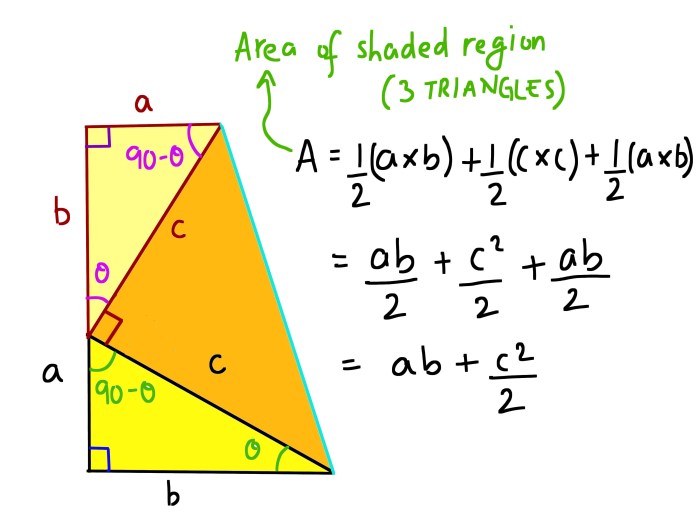
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental theorem in geometry that states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
Mathematically, it is expressed as:
a2+ b 2= c 2
where a and b are the lengths of the two shorter sides, and c is the length of the hypotenuse.
The Pythagorean Theorem is significant because it provides a method to find the length of the unknown side of a right triangle if the lengths of the other two sides are known.
Here are some applications of the Pythagorean Theorem:
- Architecture:To calculate the height of a building or the length of a roof.
- Engineering:To determine the length of a beam or the angle of a slope.
- Navigation:To calculate the distance between two points on a map.
- Surveying:To measure the height of a mountain or the distance across a river.
Applications of Triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem
Triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem have numerous applications in various fields:
Architecture
- Triangles are used to create stable and structurally sound buildings and bridges.
- The Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate the height of buildings, the length of roofs, and the angles of slopes.
Navigation and Surveying
- Triangles are used in navigation systems to determine the position and direction of ships and aircraft.
- The Pythagorean Theorem is used to calculate the distance between two points on a map or the height of a mountain.
Engineering and Design
- Triangles are used in the design of bridges, airplanes, and other structures.
- The Pythagorean Theorem is used to determine the length of beams, the angle of slopes, and the strength of materials.
Historical Development of Triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem
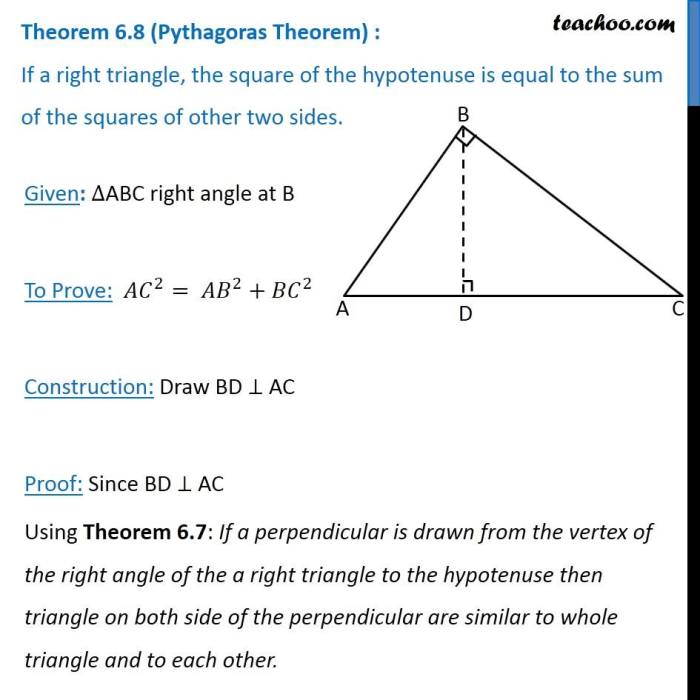
The concept of triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem has a rich historical development:
- The Babylonians knew about the Pythagorean Theorem around 1900 BC, but they did not have a general formula for it.
- The Pythagorean Theorem is attributed to the Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who is said to have discovered it around 530 BC.
- Euclid provided a formal proof of the Pythagorean Theorem in his Elements around 300 BC.
- The Pythagorean Theorem has had a significant impact on the development of mathematics and science.
Extensions and Advancements: Course 3 Chapter 5 Triangles And The Pythagorean Theorem
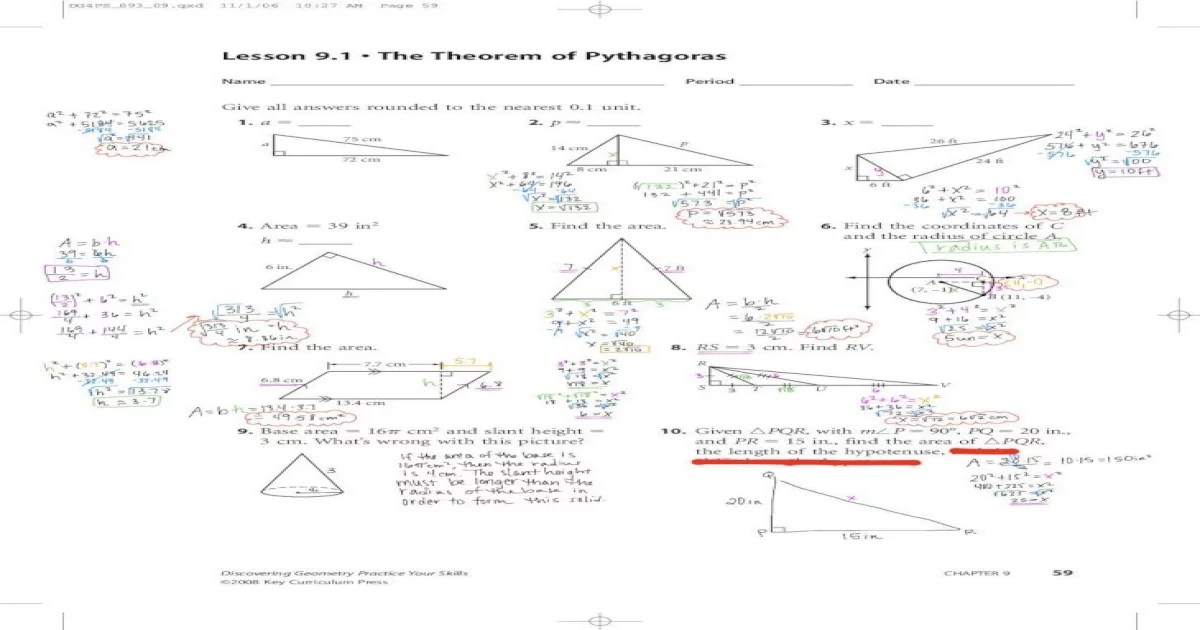
The concept of triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem has been extended and advanced in various ways:
Similar Triangles, Course 3 chapter 5 triangles and the pythagorean theorem
- Similar triangles are triangles that have the same shape but different sizes.
- The Pythagorean Theorem can be used to prove that the ratio of the corresponding sides of similar triangles is equal.
Trigonometry
- Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles.
- The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental theorem in trigonometry.
Popular Questions
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
How is the Pythagorean Theorem used in real-world applications?
The Pythagorean Theorem has numerous practical applications, including architecture, navigation, surveying, engineering, and design. It allows us to calculate distances, heights, and angles in a wide range of scenarios.
What are some historical developments related to triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem?
The concept of triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem has a rich history, with contributions from ancient mathematicians such as Thales, Pythagoras, and Euclid. Their discoveries laid the foundation for the development of geometry and trigonometry.