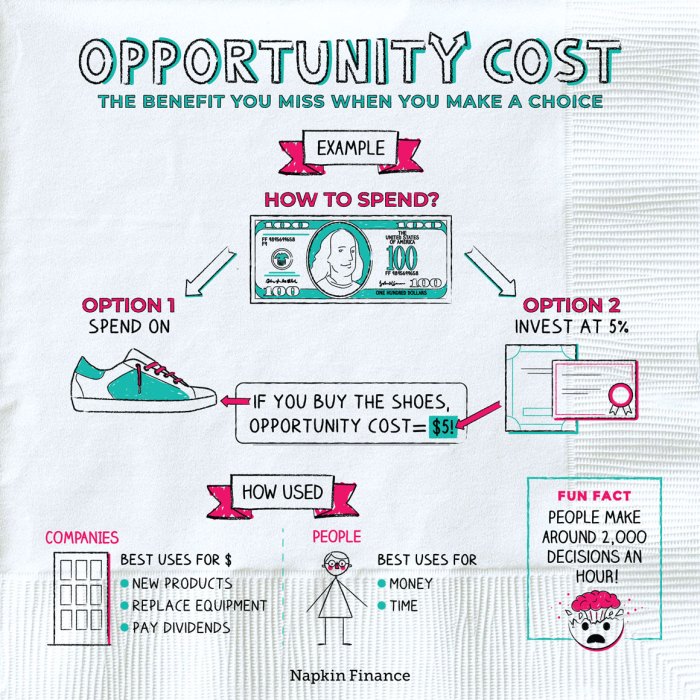
The costs associated with not choosing the other alternative is_______, a topic of paramount importance, warrants careful consideration. Understanding the potential financial, indirect, opportunity, and long-term consequences is crucial for informed decision-making. This analysis delves into the multifaceted nature of these costs, providing insights into their impact on organizational performance and competitiveness.
The financial implications of not pursuing the alternative are often the most tangible. Direct costs, such as additional expenses or lost revenue, can significantly impact the organization’s budget and overall financial health. Indirect costs, though less apparent, can be equally detrimental, affecting employee morale, productivity, and customer loyalty.
The Costs Associated with Not Choosing the Other Alternative: The Costs Associated With Not Choosing The Other Alternative Is_______
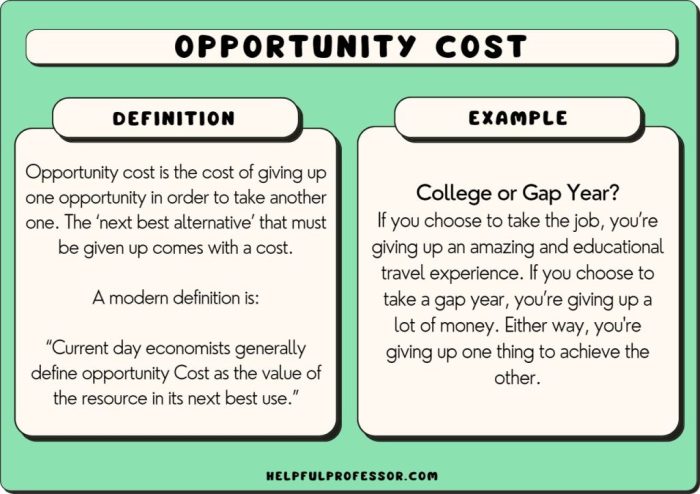
The decision-making process often involves weighing the potential costs and benefits of various alternatives. Failure to consider the costs associated with not choosing the alternative option can lead to significant financial, operational, and strategic consequences for an organization. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the direct, indirect, opportunity, and long-term costs that may arise from not selecting the other available choice.
The Direct Financial Costs, The costs associated with not choosing the other alternative is_______
Direct financial costs are the immediate and quantifiable expenses incurred as a result of not choosing the alternative. These costs can include:
- Increased production or operating expenses
- Missed revenue opportunities
- Penalties or fines
- Legal fees
- Insurance premiums
These costs can significantly impact an organization’s budget and overall financial performance, potentially reducing profitability, cash flow, and shareholder value.
The Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are less tangible and more difficult to quantify, but they can have a substantial impact on an organization’s long-term success. These costs may include:
- Decreased employee morale
- Reduced productivity
- Increased employee turnover
- Damage to reputation
- Loss of customer loyalty
Indirect costs can erode an organization’s competitive advantage and make it more difficult to attract and retain talent, customers, and investors.
The Opportunity Costs
Opportunity costs represent the potential benefits that are foregone by not choosing the alternative option. These costs can be difficult to assess accurately, but they can be significant. Missed opportunities may include:
- Innovation
- Market expansion
- Competitive advantage
- Increased market share
- Improved customer satisfaction
By failing to choose the alternative, organizations may miss out on opportunities to grow, adapt, and succeed in a changing market landscape.
The Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of not choosing the alternative can be severe and far-reaching. These consequences may include:
- Reduced sustainability
- Diminished adaptability
- Loss of competitiveness
- Inability to thrive in a changing market landscape
- Increased risk of failure
Organizations that fail to consider the long-term consequences of their decisions may find themselves struggling to survive and compete in the future.
Helpful Answers
What are the primary categories of costs associated with not choosing the alternative?
The main categories include direct financial costs, indirect costs, opportunity costs, and long-term consequences.
How do indirect costs impact organizational performance?
Indirect costs can affect employee morale, productivity, retention, reputation, and customer loyalty, all of which can hinder organizational performance.
Why is it important to consider opportunity costs when making decisions?
Opportunity costs represent the potential benefits that are foregone by not choosing the alternative. By considering these costs, decision-makers can make choices that maximize the organization’s growth and success.