Delve into the captivating world of cell division with Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Mitosis Answer Key, an invaluable resource that unlocks the mysteries of mitosis. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the video, unraveling the key concepts and offering an in-depth exploration of the intricate process of cell division.
Through engaging explanations and insightful analysis, this answer key empowers learners to grasp the complexities of mitosis, from the behavior of chromosomes to the significance of cytokinesis. Prepare to embark on a journey of scientific discovery, gaining a profound understanding of this fundamental biological process.
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Mitosis: Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Of Mitosis Answer Key
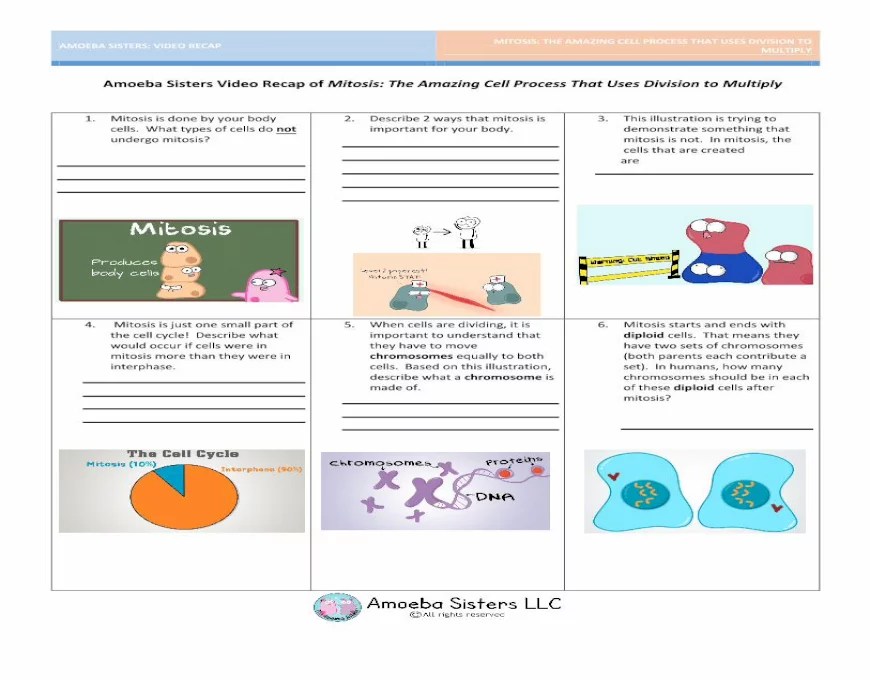
The Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Mitosis provides a concise and engaging overview of the process of mitosis. The video covers the key concepts of mitosis, including the stages of mitosis, chromosome behavior, cytokinesis, and the importance of mitosis in living organisms.
Mitosis Process
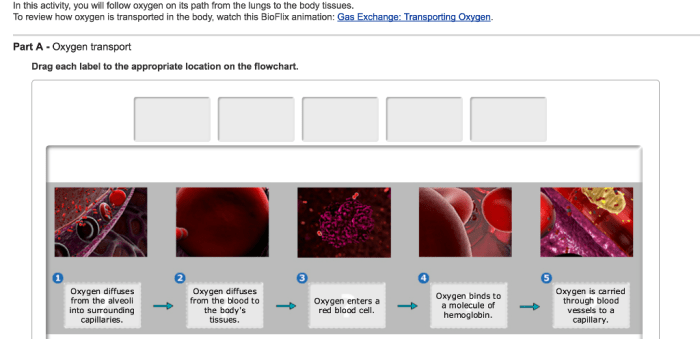
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It is a continuous process, but it can be divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Prophase:During prophase, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope begins to break down.
- Metaphase:During metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase:During anaphase, the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase:During telophase, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Chromosome Behavior
During mitosis, the chromosomes are duplicated and then separated into two identical sets. The duplicated chromosomes are called sister chromatids. The sister chromatids are held together by a structure called the centromere.
During metaphase, the sister chromatids line up in the center of the cell. The centromeres of the sister chromatids are attached to microtubules, which are fibers that pull the sister chromatids to opposite ends of the cell during anaphase.
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process by which the cytoplasm of a cell is divided into two daughter cells. Cytokinesis occurs after telophase and is different in animal and plant cells.
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs by a process called cleavage furrowing. During cleavage furrowing, a groove forms in the cell membrane and pinches the cell into two daughter cells.
In plant cells, cytokinesis occurs by a process called cell plate formation. During cell plate formation, a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.
Importance of Mitosis, Amoeba sisters video recap of mitosis answer key
Mitosis is essential for the growth, development, and repair of living organisms. Mitosis allows a cell to divide into two identical daughter cells, which can then go on to divide and form new cells. This process is essential for the growth of new tissues and organs, as well as the repair of damaged tissues.
Mitosis also plays a role in asexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, a single organism can produce offspring without the need for a mate. Mitosis allows the parent organism to create genetically identical offspring.
Essential FAQs
What is the purpose of mitosis?
Mitosis plays a crucial role in growth, development, and repair of living organisms. It ensures the production of genetically identical daughter cells, maintaining the integrity of the organism’s genetic material.
How many stages are there in mitosis?
Mitosis consists of four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Each stage involves specific chromosomal movements and changes in the cell’s structure.
What is the role of chromosomes in mitosis?
Chromosomes, which carry genetic information, condense and align during mitosis. They are separated and distributed equally to the daughter cells, ensuring that each new cell receives a complete set of genetic material.