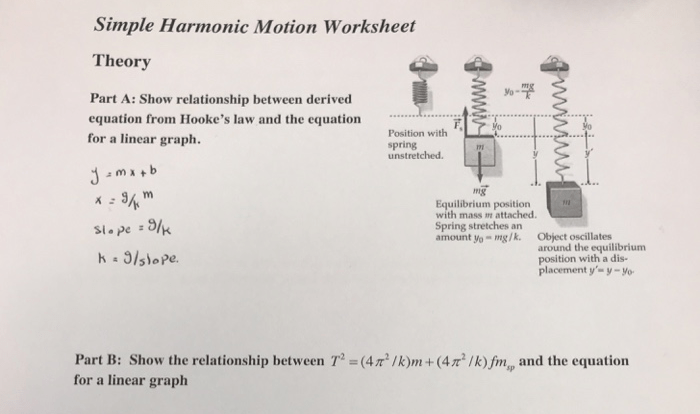
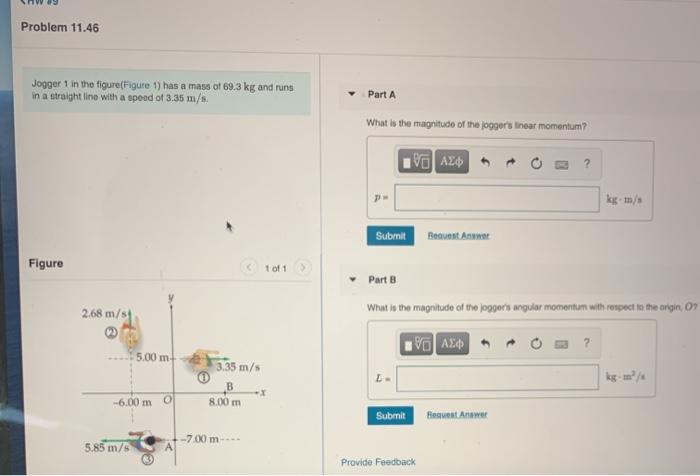
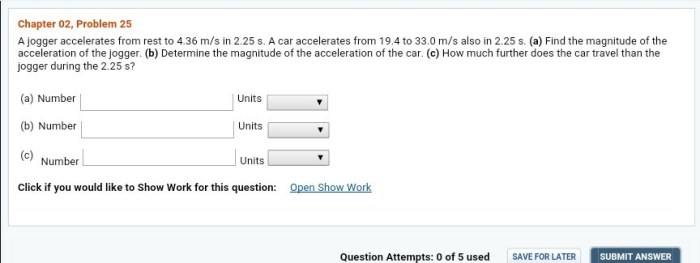
In the realm of physics, a jogger accelerates from rest to 3.0m/s in 2.0s, captivating our attention and inviting us to delve into the intricacies of motion and acceleration. This scenario serves as a cornerstone for understanding the fundamental principles governing the dynamics of objects.
As we embark on this intellectual journey, we will unravel the concepts of initial conditions, acceleration, and distance traveled. We will construct velocity-time and acceleration-time graphs, providing visual representations of the jogger’s motion. Through meticulous calculations and insightful analysis, we aim to shed light on the intricacies of this intriguing phenomenon.
Initial Conditions: A Jogger Accelerates From Rest To 3.0m/s In 2.0s
Initial conditions refer to the state of an object at the beginning of a given motion or event. In this context, the jogger is initially at rest, which means their velocity is zero at the start of the motion.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. The formula for acceleration is:
a = (v
u) / t
where:
- a is the acceleration
- v is the final velocity
- u is the initial velocity
- t is the time
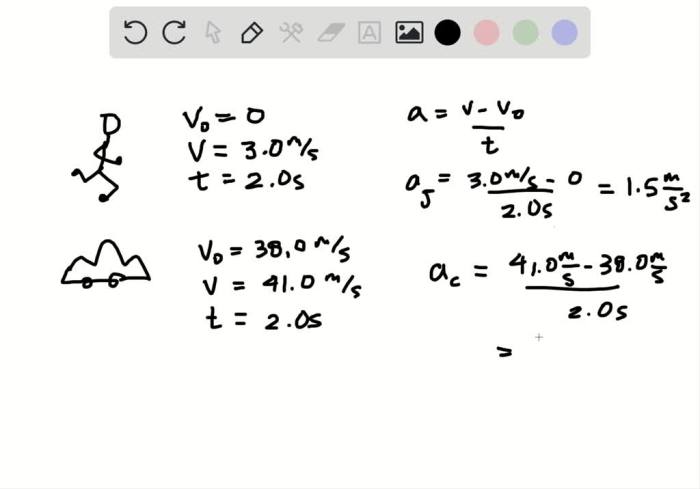
In this case, the jogger accelerates from rest (u = 0 m/s) to a final velocity of 3.0 m/s in 2.0 s. Therefore, the acceleration is:
a = (3.0 m/s
0 m/s) / 2.0 s = 1.5 m/s2
Distance Traveled

The formula for distance traveled with constant acceleration is:
d = u*t + 0.5*a*t2
where:
- d is the distance traveled
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- t is the time
In this case, the jogger starts from rest (u = 0 m/s), accelerates at 1.5 m/s 2, and travels for 2.0 s. Therefore, the distance traveled is:
d = 0 m/s
- 2.0 s + 0.5
- 1.5 m/s2
- (2.0 s) 2= 6.0 m
Velocity-Time Graph
A velocity-time graph shows the relationship between an object’s velocity and time. In this case, the jogger’s velocity-time graph is a straight line with a slope of 1.5 m/s 2. The table below shows the values of time and velocity used to plot the graph:
| Time (s) | Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 3.0 |
Acceleration-Time Graph
An acceleration-time graph shows the relationship between an object’s acceleration and time. In this case, the jogger’s acceleration-time graph is a horizontal line at 1.5 m/s 2. The table below shows the values of time and acceleration used to plot the graph:
| Time (s) | Acceleration (m/s2) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1.5 |
| 1 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 1.5 |
FAQ
What is the initial velocity of the jogger?
0 m/s (rest)
What is the acceleration of the jogger?
1.5 m/s^2
What is the distance traveled by the jogger in 2 seconds?
6.0 meters