Embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of invasive species with our comprehensive Invasive Species Worksheet Answer Key. This invaluable resource empowers you with the knowledge and understanding to combat the detrimental impacts of these ecological disruptors.
Delve into the origins, characteristics, and profound effects of invasive species on ecosystems. Discover innovative methods for their identification and explore effective management and control strategies. Engage with case studies and best practices to prevent the spread of these environmental threats.
Invasive Species Worksheet Answer Key
An invasive species worksheet answer key is an essential tool for students, teachers, and conservationists. It provides correct answers to questions and exercises related to invasive species, facilitating effective learning and understanding of this critical environmental issue.
The answer key typically includes a table with columns for species name, origin, impact, and management strategies. This comprehensive format allows users to quickly identify key information about invasive species, assess their potential risks, and develop appropriate management plans.
Detailed Table of Invasive Species
| Species Name | Origin | Impact | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) | Eastern Europe | – Fouls water intake pipes and structures
|
– Physical removal
|
| Kudzu (Pueraria lobata) | Japan | – Forms dense thickets that smother native vegetation
|
– Manual removal
|
| Asian Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) | China | – Competes with native fish for food and habitat
|
– Electrical barriers
|
| Emerald Ash Borer (Agrilus planipennis) | Asia | – Kills ash trees by feeding on their inner bark
|
– Chemical control
|
Key Concepts and Definitions
Understanding the concept of invasive species and their ecological impacts is crucial for effective ecosystem management and conservation efforts.
An invasive species is a non-native organism that has been introduced into an ecosystem and poses a threat to native biodiversity and ecosystem stability. These species often exhibit aggressive growth patterns, outcompeting native species for resources and disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Ecological Niches
Every species occupies a specific ecological niche within an ecosystem, encompassing its role, habitat, and interactions with other organisms. Invasive species can disrupt these niches by:
- Competing with native species for food, water, and other resources
- Preying on native species, reducing their populations
- Introducing diseases or parasites that can decimate native populations
- Altering habitat conditions, making them less suitable for native species
Examples of Invasive Species and Their Impacts, Invasive species worksheet answer key
Numerous invasive species have caused significant ecological damage worldwide. Some notable examples include:
- Kudzu (Pueraria montana) : A rapidly growing vine native to Japan that has become invasive in the southeastern United States, smothering native vegetation and disrupting ecosystems.
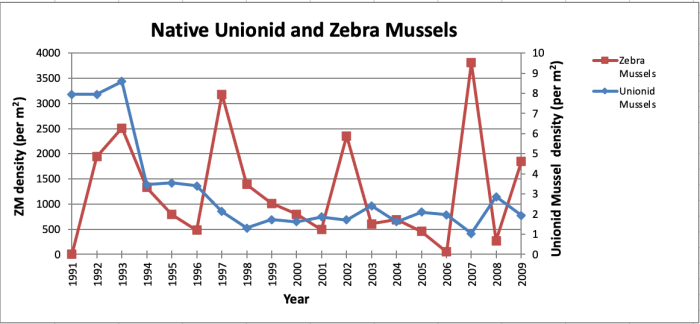
- Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) : A freshwater mollusk that has invaded North American lakes and rivers, clogging water intake systems and competing with native mussels for food.
- European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) : Introduced to Australia in the 1800s, rabbits have become a major pest, overgrazing vegetation and contributing to soil erosion.
These examples highlight the devastating impacts that invasive species can have on ecosystems, underscoring the need for effective management and control measures to protect native biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Methods for Identifying Invasive Species
Identifying and monitoring invasive species is crucial for effective management and prevention strategies. Various methods are employed to detect and track these non-native species, including field surveys, remote sensing, and molecular techniques.
Field Surveys
Field surveys involve physical observations and data collection in the field. Researchers conduct visual assessments, collect samples, and record species distribution, abundance, and habitat characteristics. This method provides detailed information about the presence, spread, and potential impacts of invasive species.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing utilizes satellite imagery, aerial photography, and other technologies to monitor large areas and detect changes in vegetation patterns. By analyzing spectral signatures, researchers can identify invasive species that differ in their reflectance properties from native vegetation.
Molecular Techniques
Molecular techniques, such as DNA barcoding and genetic sequencing, enable precise identification of invasive species, especially when morphological identification is challenging. These techniques analyze genetic markers to differentiate between closely related species and track the spread and genetic diversity of invasive populations.
- Key Indicators for Identifying Potential Invasive Species:
- Rapid population growth and spread
- Lack of natural predators or competitors
- Tolerance to a wide range of environmental conditions
- Ability to hybridize with native species
- Negative impacts on ecosystem structure and function
Management and Control Strategies
Managing and controlling invasive species requires a multifaceted approach that involves various strategies. These strategies aim to prevent the introduction and establishment of invasive species, mitigate their impacts, and restore affected ecosystems.
Invasive species management strategies can be categorized into four main types: physical, chemical, biological, and integrated pest management (IPM).
Physical Control Methods
Physical control methods involve the use of physical barriers or techniques to prevent the spread or eliminate invasive species. These methods include:
- Manual removal:Hand-pulling, digging, or cutting invasive plants.
- Mechanical removal:Using machinery or tools to remove invasive plants or animals.
- Physical barriers:Constructing fences, walls, or other structures to prevent the movement of invasive species.
Chemical Control Methods
Chemical control methods involve the use of herbicides, pesticides, or other chemicals to kill or suppress invasive species. These methods include:
- Herbicides:Chemicals used to kill or control invasive plants.
- Pesticides:Chemicals used to kill or control invasive animals.
- Biological control agents:Living organisms, such as predators, parasites, or pathogens, that are introduced to control invasive species.
Biological Control Methods
Biological control methods involve the use of living organisms to control invasive species. These methods include:
- Classical biological control:Introducing non-native natural enemies to control invasive species.
- Augmentative biological control:Releasing additional natural enemies to supplement existing populations.
- Conservation biological control:Managing or enhancing natural enemies to control invasive species.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a holistic approach that combines multiple control methods to manage invasive species. IPM programs typically involve a combination of physical, chemical, and biological control methods, as well as cultural practices and monitoring.
Case Studies of Successful Invasive Species Management Programs
Numerous successful invasive species management programs have been implemented worldwide. Here are a few notable examples:
- Control of the invasive cane toad in Australia:A combination of physical removal, chemical control, and biological control using a native fungus has significantly reduced cane toad populations in some areas.
- Eradication of the invasive giant African snail in Florida:A comprehensive IPM program involving chemical control, biological control, and community engagement has successfully eradicated the giant African snail from Florida.
- Management of the invasive water hyacinth in Lake Victoria:Biological control using the water hyacinth weevil has effectively controlled the spread of water hyacinth in Lake Victoria, reducing its negative impacts on fisheries and navigation.
Education and Public Awareness
Educating the public about invasive species is crucial because it empowers individuals to recognize, report, and prevent the spread of these harmful organisms. By raising awareness, we can collectively minimize the ecological and economic impacts caused by invasive species.
Key Educational Materials and Resources
The following table highlights key educational materials and resources tailored to different target audiences:
| Target Audience | Materials/Resources |
|---|---|
| General Public | – Brochures and fact sheets
|
| Landowners and Land Managers | – Technical guides and manuals
|
| Educators and Students | – Curricula and lesson plans
|
Best Practices for Preventing the Spread of Invasive Species
- Clean and inspect boats, trailers, and gear before entering and leaving water bodies.
- Avoid transporting firewood from one location to another.
- Dispose of unwanted plants and animals responsibly (e.g., composting, garbage disposal).
- Plant native species in gardens and landscapes.
- Support organizations and initiatives dedicated to invasive species management.
- Report sightings of invasive species to local authorities or designated reporting channels.
General Inquiries: Invasive Species Worksheet Answer Key
What is the significance of an invasive species worksheet answer key?
It provides a structured and comprehensive guide to understanding the key concepts, definitions, methods, and strategies related to invasive species.
How can I use the invasive species worksheet answer key?
Use it as a study guide, reference material, or educational tool to enhance your knowledge and understanding of invasive species.
What are some examples of well-known invasive species?
Examples include the zebra mussel, kudzu vine, and Burmese python.